Osteoporosis and Bone Health: Exercises and Rehabilitation
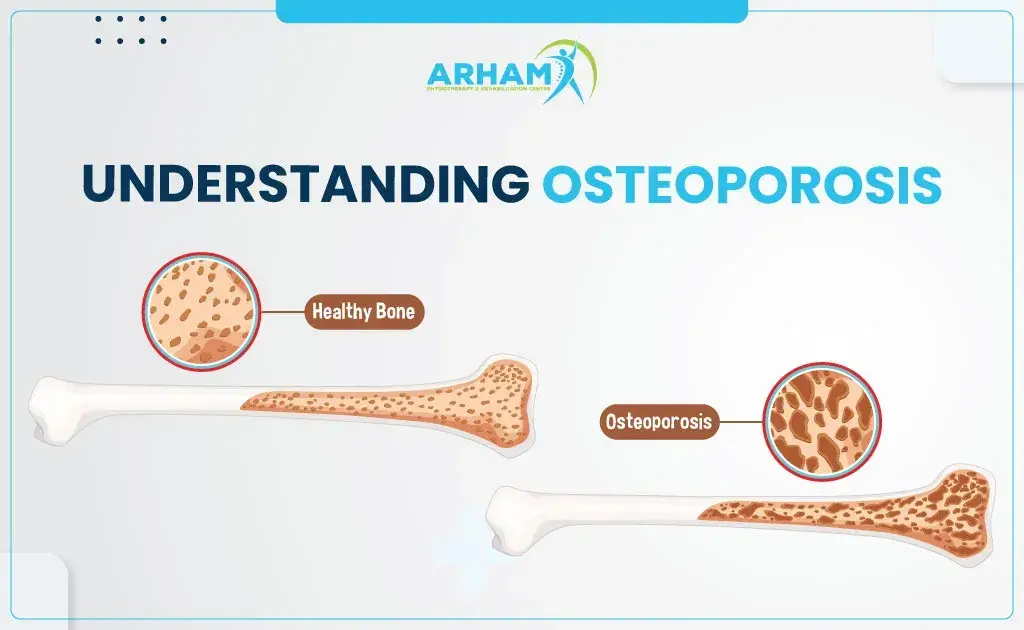
Understanding Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a silent, often underestimated, and potentially debilitating condition affecting millions worldwide, particularly as they age. At its core, osteoporosis is characterized by weakened bones, making them fragile and prone to fractures. Understanding the intricacies of osteoporosis is essential to grasp the significance of bone health and the steps necessary to prevent and manage this condition effectively.
The Importance of Bone Health
Bones are the silent scaffolding that supports our bodies, allowing us to move, stand tall, and carry out everyday activities. Yet, the significance of bone health often needs to be noticed until issues arise. Bone health isn’t just about having strong bones; it’s about ensuring that bones maintain their density and strength over time.
Strong and healthy bones are vital for physical well-being and play a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Here are some key aspects highlighting the importance of bone health:
- Structural Integrity: Bones support our bodies, ensuring we can stand, walk, run, and perform various physical tasks. Solid bones make everyday activities manageable, and the risk of fractures increases.
- Protection for Organs: Bones act as protective shields for vital organs. For instance, the ribcage safeguards the heart and lungs, while the skull protects the brain. Maintaining bone density is essential to ensure this protective function.
- Mineral Storage: Bones serve as a reservoir for essential minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus. When our bodies need these minerals for various functions, bones release them into the bloodstream. Maintaining adequate mineral levels in bones is crucial for overall health.
- Blood Cell Production: Bone marrow, the soft, spongy tissue within bones, produces blood cells, including red blood cells that transport oxygen and white blood cells that fight infection. Healthy bone marrow is essential for maintaining a robust immune system.
- Posture and Mobility: Strong bones are essential for maintaining good posture and mobility. They allow us to stand tall, walk quickly, and perform activities without discomfort or limitations.
Understanding the vital role bones play in our overall health underscores the importance of bone health maintenance. Osteoporosis, characterised by the gradual loss of bone density and quality, can lead to fractures, pain, and a diminished quality of life. However, the good news is that osteoporosis is preventable and manageable with the proper knowledge and lifestyle choices.
Risk Factors and Prevention

Identifying Risk Factors:
1. Age:
- Risk Factor: Aging is one of the primary risk factors for osteoporosis.
- Why: As you age, bone density naturally decreases, making bones more susceptible to fractures.
2. Gender:
- Risk Factor: Women are at a higher risk of osteoporosis compared to men.
- Why: Women typically have lower bone density, and the hormonal changes during menopause accelerate bone loss.
3. Family History:
- Risk Factor: A family history of osteoporosis or fractures increases your risk.
- Why: Genetics plays a role in determining bone density and susceptibility to fractures.
4. Low Body Weight:
- Risk Factor: Individuals with a low body mass index (BMI) are at increased risk.
- Why: Lower body weight often means lower bone mass.
5. Hormonal Changes:
- Risk Factor: Hormonal imbalances, such as those occurring in menopause or due to certain medical conditions, can lead to bone loss.
- Why: Hormones like oestrogen play a critical role in bone health.
6. Dietary Factors:
- Risk Factor: Inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D.
- Why: These nutrients are essential for building and maintaining strong bones.
7. Sedentary Lifestyle:
- Risk Factor: Lack of weight-bearing exercise.
- Why: Weight-bearing exercises help stimulate bone formation and improve bone density.
8. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption:
- Risk Factor: Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake can weaken bones.
- Why: These substances negatively impact bone health.
9. Medications:
- Risk Factor: Certain medications, such as long-term use of corticosteroids, can lead to bone loss.
- Why: These drugs interfere with the bone remodelling process.
Strategies for Osteoporosis Prevention:
1. Balanced Diet:
- Consume a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D through dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods, and supplements if necessary.
2. Regular Exercise:
- Engage in weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, dancing, and resistance training to build and strengthen bones.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Quit smoking to protect bone health.
- Limit alcohol consumption to a moderate level.
4. Bone Density Testing:
- Discuss bone density testing with your healthcare provider, especially if you have multiple risk factors.
5. Medication when Necessary:
- Consult your doctor about medications for osteoporosis if you have a high risk profile.
6. Fall Prevention:
- Make your living environment safer by removing tripping hazards and using assistive devices if needed.
- Diagnosis and Assessment
Bone Density Tests: The Cornerstone of Diagnosis
Bone density tests, also known as densitometry or DXA scans (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry), are the gold standard for diagnosing osteoporosis and assessing bone density. Here’s what you need to know:
1. How It Works:
- DXA scans use a minimal amount of X-rays to measure bone mineral density (BMD) at specific sites, such as the hip, spine, and wrist.
- The results are compared to the average BMD of healthy young adults, known as a T-score, to determine bone health.
2. Who Should Get Tested:
- Postmenopausal women and men aged 50 and older should consider bone density testing, especially if they have risk factors.
- Younger individuals with significant risk factors like long-term steroid use or a history of fractures may also be candidates.
3. Frequency:
- In general, testing may be done every one to two years for those with low bone density or other risk factors.
Assessing Fracture Risk: Beyond Bone Density
While bone density tests are essential, they don’t tell the whole story. Assessing fracture risk
Involves Considering other factors:
1. Clinical Risk Factors:
- A healthcare provider will evaluate factors like age, gender, family history, and previous fractures to assess overall risk.
2. FRAX® Tool:
- The FRAX® tool is a widely used assessment tool that calculates an individual’s ten-year risk of major osteoporotic fractures or hip fractures.
- It incorporates clinical risk factors and BMD results, providing a comprehensive risk assessment.
3. Vertebral Fracture Assessment (VFA):
- VFA is a specialised X-ray technique used to detect vertebral fractures, which are common in osteoporosis.
- Identifying these fractures can guide treatment decisions.
The Role of Exercise in Bone Health:

Exercise is a cornerstone in the prevention and management of osteoporosis. It offers numerous benefits for bone health, including:
1. Bone Density Improvement:
- Weight-bearing exercises, in particular, stimulate the production of new bone tissue, enhancing bone density and strength.
2. Muscle Strengthening:
- Resistance exercises and strength training not only build muscle but also indirectly support bone health by improving balance and reducing the risk of falls.
3. Improved Balance and Coordination:
- Flexibility and balance exercises, like yoga and Tai Chi, enhance stability, reducing the likelihood of falls and fractures.
4. Posture Enhancement:
- Exercises that target the core and back muscles can help improve posture, reducing the risk of vertebral fractures.
5. Enhanced Joint Mobility:
- Regular exercise promotes joint health and mobility, ensuring that individuals can move comfortably and confidently.
Types of Exercises for Osteoporosis:
When it comes to osteoporosis, not all exercises are created equal. Some are particularly beneficial for bone health:
1. Weight-Bearing Exercises:
- These activities require you to support your body’s weight, such as walking, hiking, dancing, and stair climbing.
2. Strength Training:
- Strength training exercises involve resistance against a force, like weights or resistance bands.
- Focus on compound movements that work multiple muscle groups, like squats, lunges, and push-ups.
3. Flexibility and Balance Exercises:
- Yoga, Tai Chi, and Pilates are excellent choices for enhancing flexibility, balance, and posture.
- These exercises reduce the risk of falls and fractures.
4. Low-Impact Activities:
- Swimming and cycling are low-impact exercises that are gentle on the joints and can complement a bone-healthy exercise routine.
5. Consult a Professional:
- If you have osteoporosis, it’s advisable to consult a physiotherapist or certified fitness trainer who can design a customised exercise program tailored to your specific needs and limitations.
Weight-Bearing Exercises for Strong Bones
In this chapter, we will dive into the importance of weight-bearing exercises in maintaining and improving bone health.
Understanding Bone Health
- A brief overview of bone structure and its significance in overall health.
- The role of bone density in determining bone health.
What Are Weight-Bearing Exercises?
- Definition and examples of weight-bearing exercises.
- How these exercises stimulate bone growth and density.
Benefits of Weight-Bearing Exercises
- Beyond bone health: the additional advantages of weight-bearing exercises, including improved cardiovascular health and weight management.
Incorporating Weight-Bearing Exercises into Your Routine
- Practical tips on integrating weight-bearing exercises into your daily life.
- Recommendations for frequency and duration.
Strength Training for Bone Health and Muscle Building
This chapter explores strength training exercises that not only build muscle but also contribute to better bone health.
The Synergy Between Muscle and Bone
- How strength training impacts bone density and overall bone health.
- The interplay between muscle strength and bone strength.
Types of Strength Training Exercises
- An overview of strength training exercises, including bodyweight exercises and resistance training.
- The role of compound exercises in engaging multiple muscle groups.
Creating a Strength Training Routine
- Building a personalised strength training program based on your fitness goals.
- Safety precautions and proper techniques to prevent injury.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises for Mobility and Stability
The Importance of Flexibility
- Understanding the role of flexibility in joint health and range of motion.
- How improved flexibility contributes to better posture.
Benefits of Balance Training
- The advantages of balance exercises in preventing falls and reducing the risk of injuries.
- Balance as a key component of functional fitness.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation and physical therapy are dynamic fields in the realm of healthcare, dedicated to restoring and enhancing the physical capabilities, mobility, and quality of life of individuals affected by injury, illness, or disability. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the vital roles of rehabilitation and physical therapy, shedding light on the principles, techniques, and benefits of these crucial healthcare disciplines.
Diet and Nutrition for Strong Bones: Building a Foundation of Health
Strong and healthy bones are essential for overall well-being and maintaining an active lifestyle. Your bones provide structure, protect vital organs, and serve as a reservoir for essential minerals. To ensure your bones remain robust and resilient throughout life, it’s crucial to pay attention to your diet and nutrition. In this guide, we’ll explore the key nutrients and dietary practices that promote bone health, helping you build and maintain strong bones for years to come.
Medications and Treatment Options
When facing illness or health challenges, the world of medications and treatment options can appear complex and overwhelming. However, understanding these options is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare. In this guide, we’ll explore various medications and treatment modalities, shedding light on their uses, benefits, and considerations to help you navigate your path to wellness.
- Fall Prevention and Safety
They can result in serious injuries, affecting one’s mobility and independence. However, with the right knowledge and precautions, many falls can be prevented. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the importance of fall prevention and safety. If you or a loved one struggles with balance or fear of falling, this article might help you make an informed decision about which power source is best for your needs.
Conclusion
In the journey towards fall prevention and safety, we’ve explored the paramount importance of staying upright and injury-free, particularly as we age. Falls can have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only our physical health but also our emotional well-being and independence. However, armed with knowledge, awareness, and proactive strategies, we can significantly reduce the risk of falls and embrace a future free from the fear of stumbling.
